¶ Dot Voting
¶ What it is
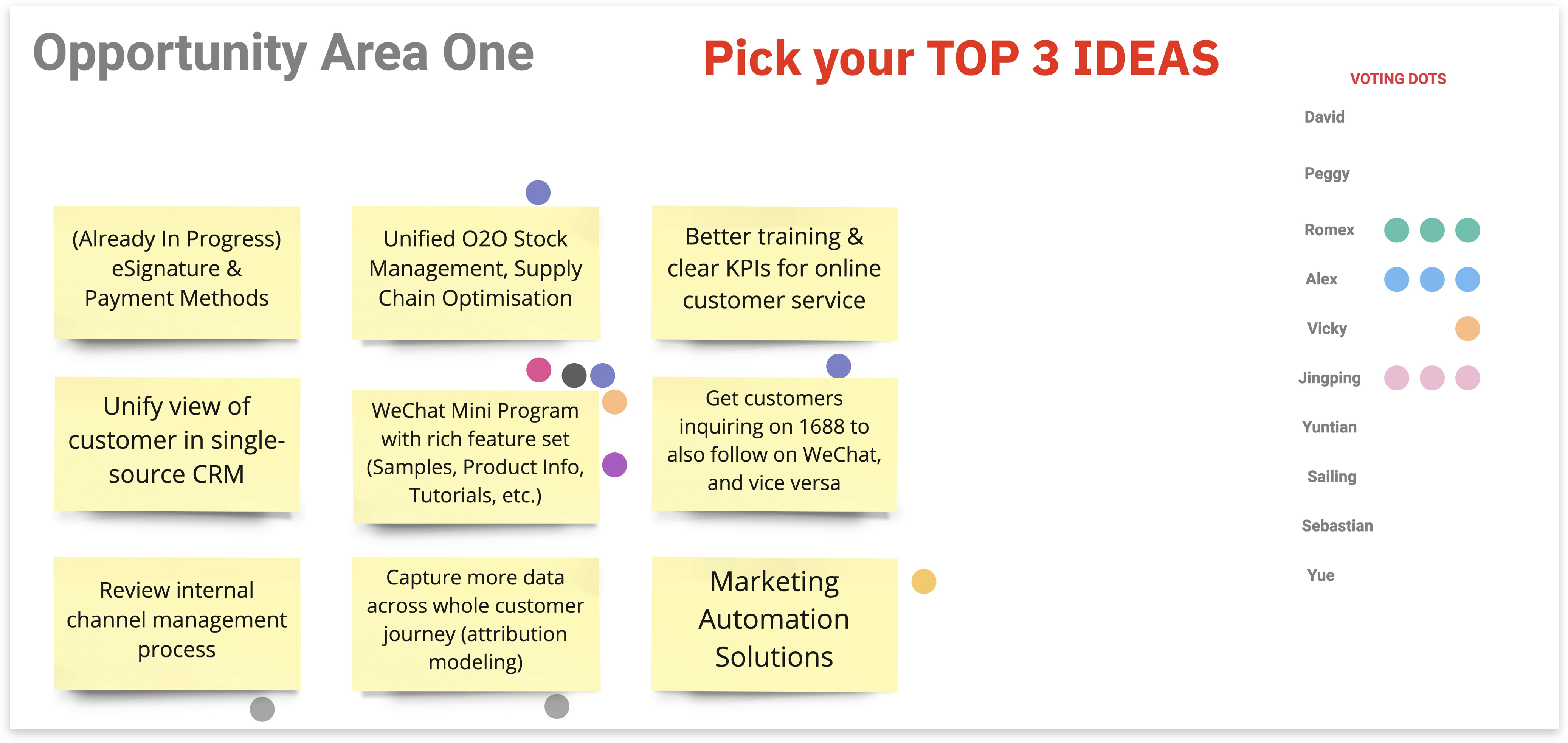
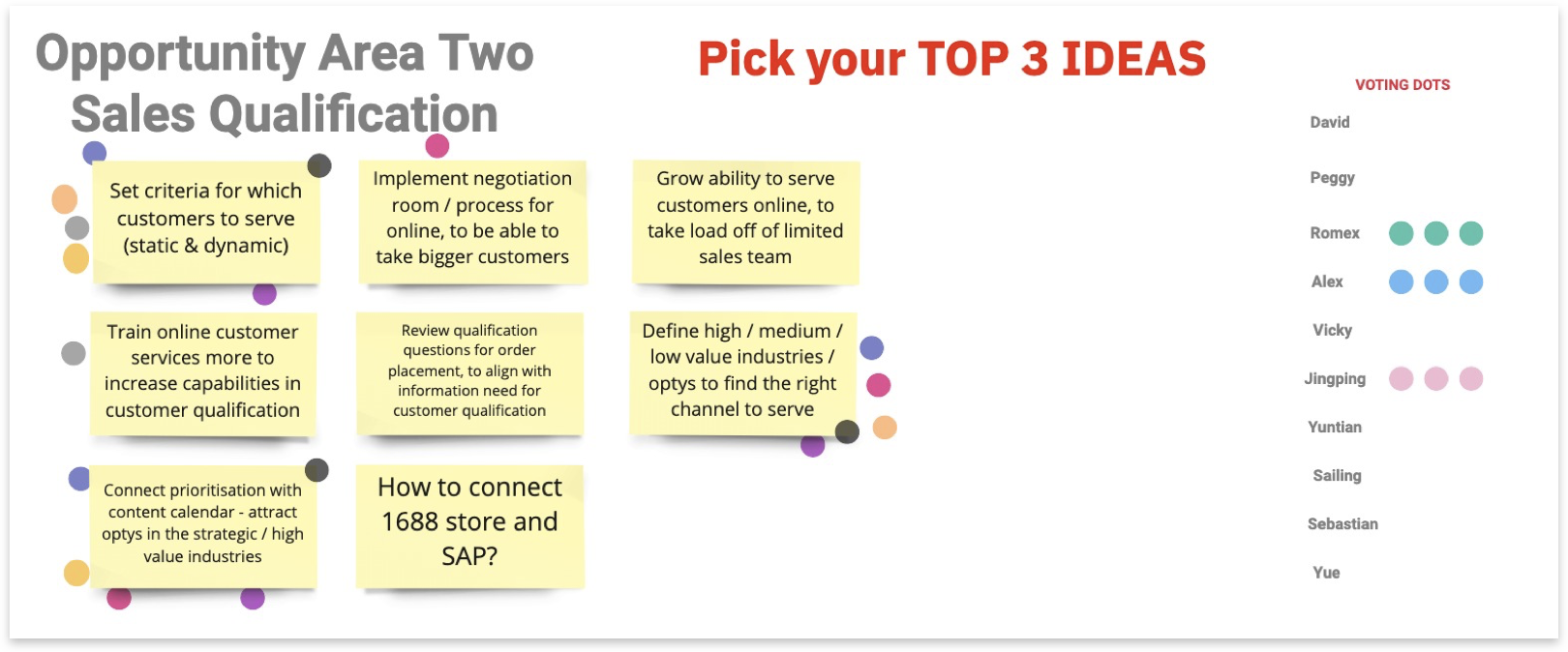
In Dot Voting, team members vote on ideas on a whiteboard by sticking a dot on the respective idea to show support or interest in that idea.
¶ Why it is useful
Dot Voting helps to evaluate and prioritize ideas on a whiteboard based on the team’s opinion. It creates a heat map of popular ideas and supports the discussion.
¶ When to use it
Dot voting can be applied in different project phases whenever you want to prioritize or narrow your choices. For example, it is widespread during the Ideation Phase as you can quickly and democratically select ideas based on specific criteria (e.g., cost, value for the customer, ease of implementation).
¶
¶ How is it done
- After generating ideas, leave the post-its with the ideas on the whiteboard.
- Give each team member the same number of sticky dots (e.g., five sticky dots per member).
- Ask everyone to read through the ideas and vote on the ones they like the most, find most interesting or consider most innovative or practical by posting their sticky dots next to these ideas.
- Look at the heat map that the dots have created and discuss the voting outcome - which ideas received the most votes? Then, let participants explain why they voted for these ideas.
- Rearrange the post-its with ideas based on popularity.
- Discuss the next steps in the team.
¶ Do's & Don't
Do's
- Instead of putting sticky dots, team members can also draw dots with a marker.
- Decide whether a team member can use more of their votes on one idea.
- To avoid group bias, let everyone think about the ideas they want to vote for and only allow them to place a dot.
- Follow up on ideas that haven’t been voted on to ensure they haven't been forgotten.
- Decide clearly on the voting criteria - most innovative ideas, most feasible ideas, most customer-centric ideas, and highest-impact ideas …?
¶ Tools needed
- Whiteboard (virtual)
- Post-its with ideas (virtual)
- Sticky dots (virtual)
¶
¶ Example
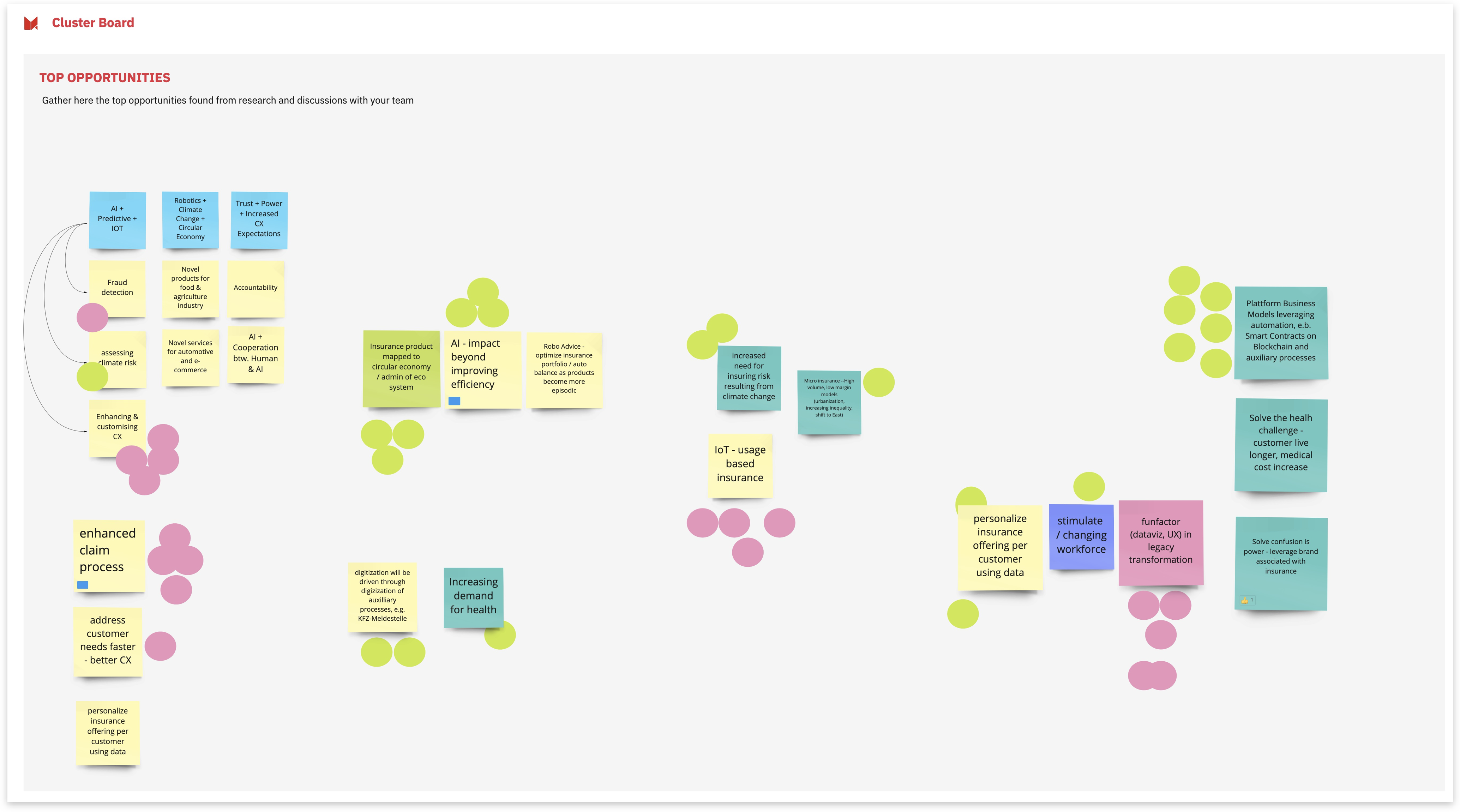
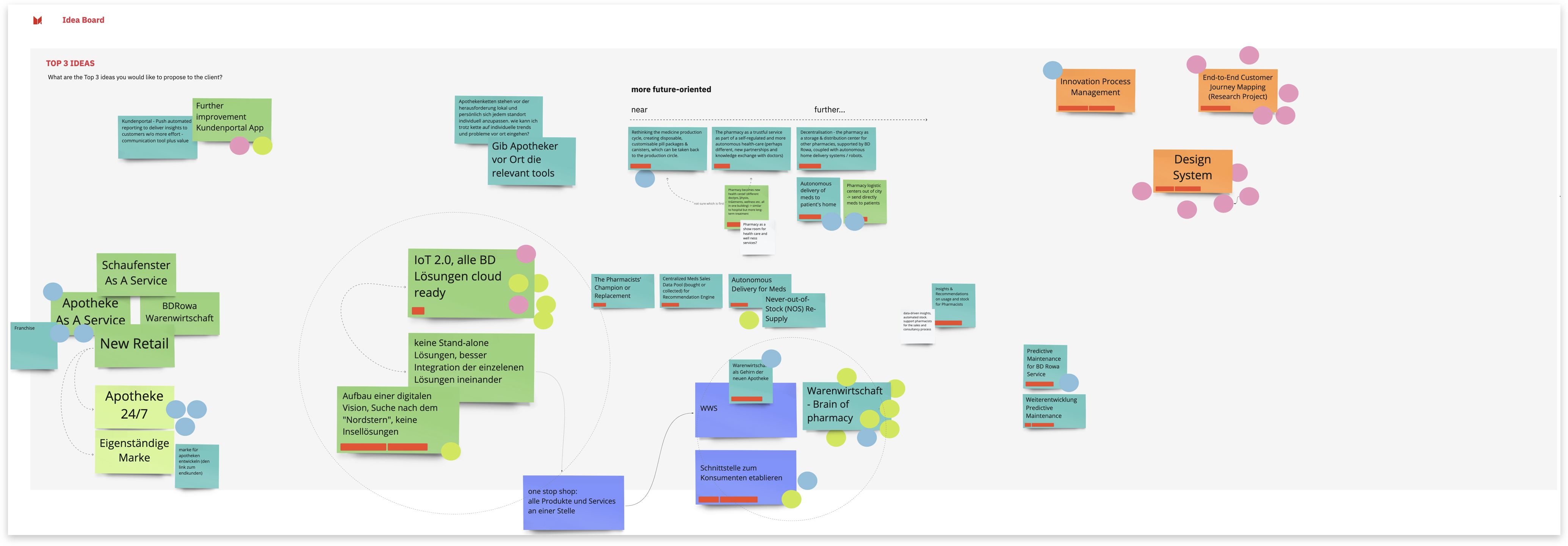
¶ Dot Voting Resources
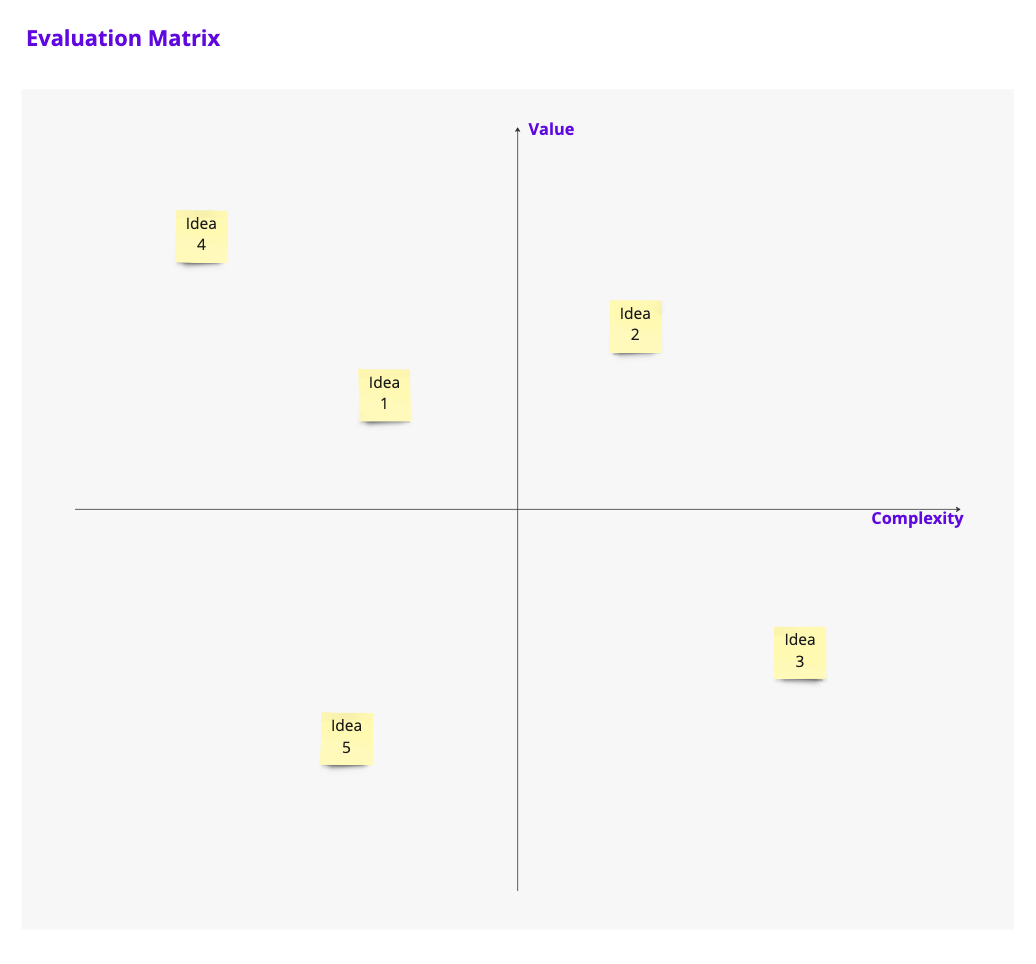
¶ Evaluation Matrix
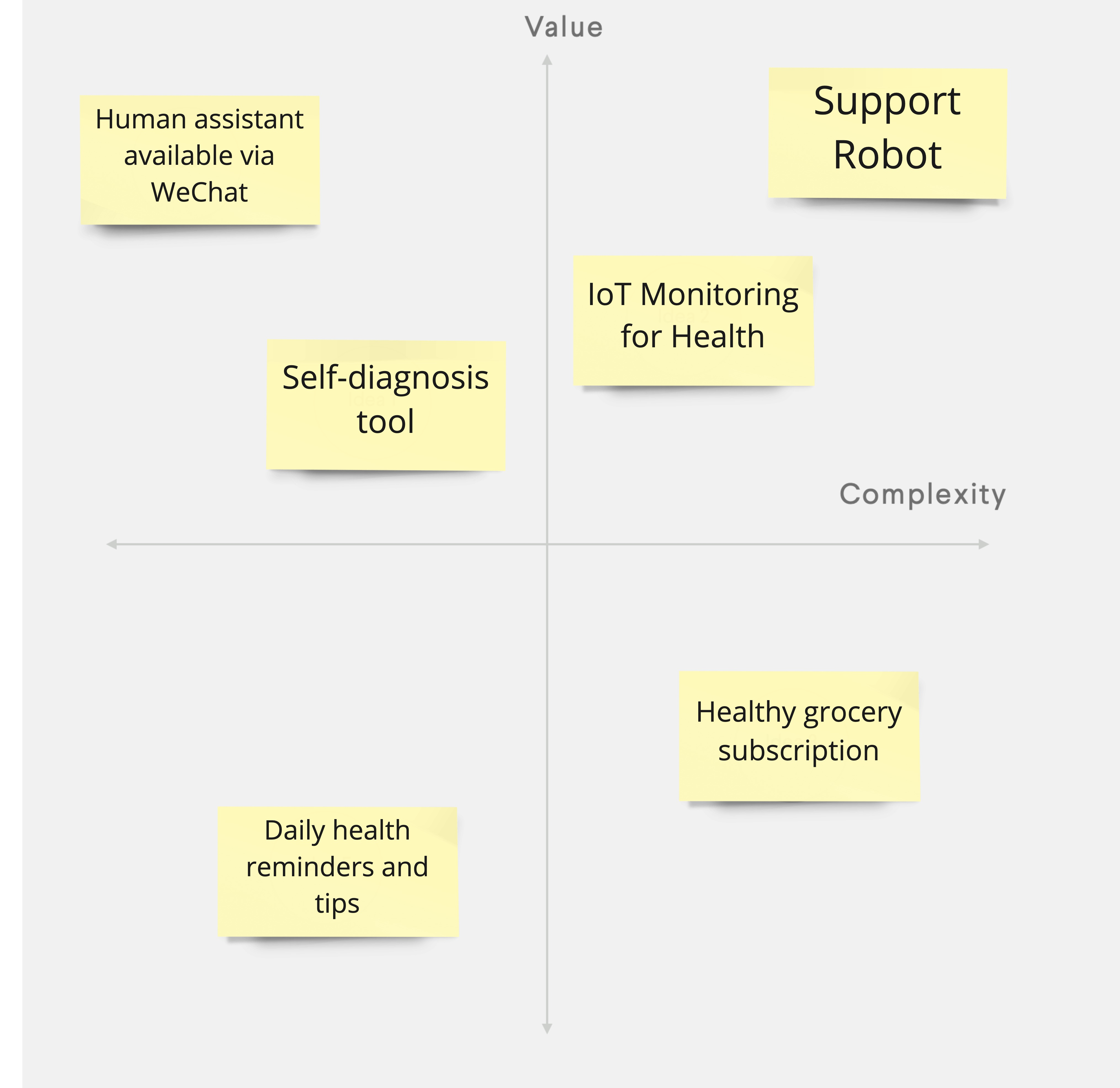
¶ What it is
The Evaluation Matrix categorises and graphically organises ideas based on two defined dimensions.
¶ Why it is useful
The Evaluation Matrix distinguishes ideas and identifies the most promising ones to prioritise them moving forward. You can spot low-hanging fruits and high-impact ideas depending on the evaluation criteria.
¶ When to use it
The Evaluation Matrix is another tool that helps you to prioritise or narrow down your choices and can be applied at different stages during a project. It allows you to select whenever you have more than one criteria to decide on.
¶
¶ How is it done
- Decide on the two evaluation criteria of your matrix.
- Draw a 2x2 matrix on a whiteboard and indicate which axis represents which dimension.
- Individually or in a team, pick the post-its with generated ideas and place them in the matrix.
- Discuss the outcome - and summarise takeaways - which ideas should be prioritised? Which are most valuable, feasible, or worth considering? Discuss the next steps.
¶ Do's & Don't
Do's
- You can use all generated ideas and place them in the matrix or the most popular ones from the Dot Voting exercise.
- Ensure that one of the dimensions in the matrix is related to implementation (e.g., complexity, resources needed), as this exercise prioritises which ideas will be developed further.
¶ Tools needed
- Whiteboard (virtual)
- Post-its with ideas (virtual)
- Markers (virtual)
¶
¶ Example